Updated July 2025: Stop error messages and fix your computer problem with this tool. Get it now at this link
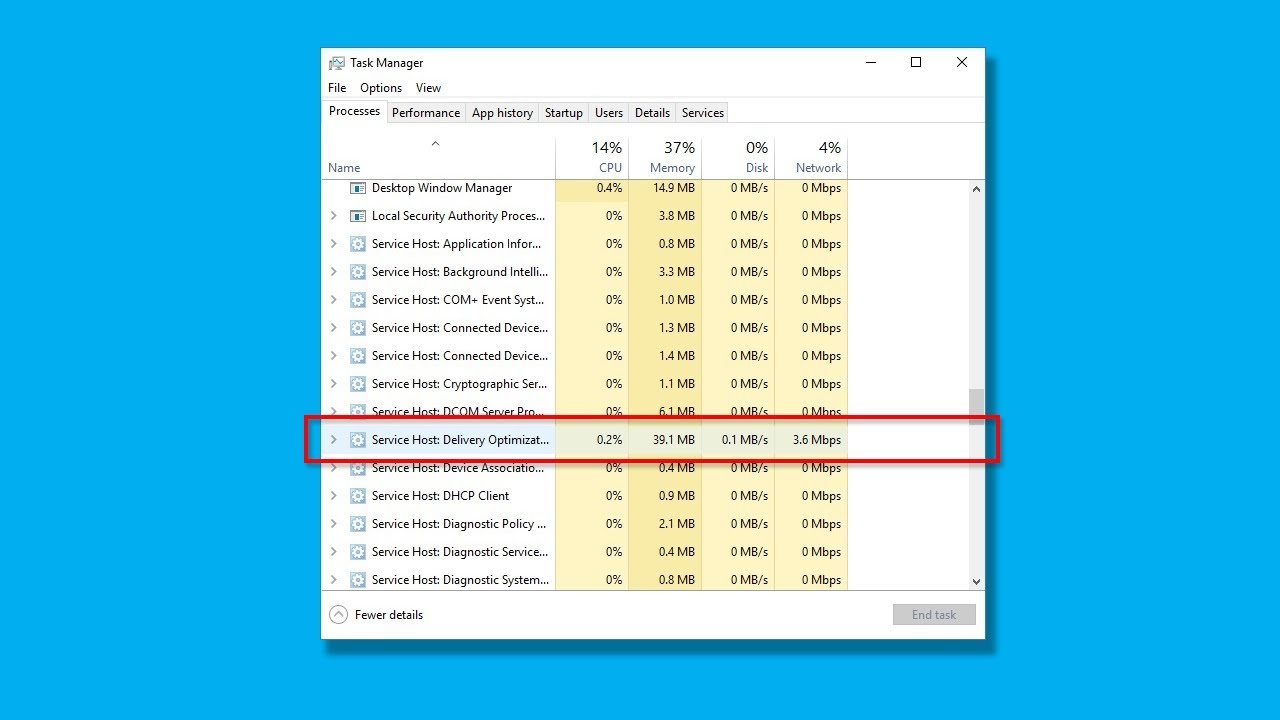
Service Host Delivery Optimization (SHDO) is a feature introduced by Microsoft in Windows Server 2012 R2. This feature allows you to deploy applications directly into virtual machines without having to install them onto physical servers. However, it does require some configuration. If you experience high CPU usage while running SHDO, there are several possible solutions.
First, check whether the problem occurs during installation or execution of the application. In most cases, the issue occurs because of the way the feature works. When you use SHDO, the operating system creates a partition within each VM. Because of this, the amount of space used by the VMs increases. During installation, the installer checks how much space is required for the OS and other components. If the space requirement exceeds what is allocated, the installer stops installing the software. To resolve this issue, you must allocate enough space to the partitions. You can do this manually or automatically. For example, you can change the default allocation size, set a maximum value, or limit the number of installations per day.
If the problem still persists, try disabling the feature. Then restart your computer. After rebooting, enable the feature again.
If the problem continues, contact the support team. They will help you find out why the feature is causing high CPU usage.
Service Host Delivery Optimization does what?
Delivery Optimization is a new Windows 10 feature that improves the download speeds of apps and games. This is done by caching files locally on the device.
Users who have been experiencing slow downs while updating their computers should consider disabling delivery optimization. There are many ways to do it. You can find out how here.
Solution 1: Stop letting downloads from other computers
This issue occurs due to an Error in Windows 10 Version 1803 or Later Versions.
1. Click “Go Back” button
2. Select Turn Off Automatic Updating
3. Restart your device
We highly recommend that you use this tool for your error. Furthermore, this tool detects and removes common computer errors, protects you from loss of files, malware, and hardware failures, and optimizes your device for maximum performance. This software will help you fix your PC problems and prevent others from happening again:
Updated: July 2025
Solution 2: Check Background Downloads
Many users complained about high CPU Usage after installing new software. They found out that there is no solution to this problem. However, you can resolve this problem by checking background downloads.
There are two ways to solve the problem. One way is cancelling all pending tasks. Another one is closing the app and reopening it again. This issue will disappear once downloading/updating process ends.
Solution 3: Change your group’s rules.
If you are having trouble getting rid of the “This computer needs to restart now” pop up, try modifying your group policy settings.
Solution 4: Perform Clean Boot
If none of the previous solutions worked, you might want to perform Clean Boot. This process removes all traces of malware from your PC. You can do this manually, or use a tool like Malwarebytes Anti-Malware Premium.
RECOMMENATION: Click here for help with Windows errors.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are there too many processes running in the background?
A background process is a program running on your PC even though it isn’t open in a window. This article explains how to find out what’s causing your system to slow down and why it happens.
The Problem With Background Processes
Windows needs to keep track of every piece of software on your machine, including those apps that aren’t actively being used. To do this, Windows uses a collection of background tasks that monitor everything happening on your PC. These tasks include things like checking email, updating your Facebook status, downloading files, and even keeping your antivirus database up to date.
As you add more and more programs to your PC over time, the number of background tasks increases too. Eventually, you’ll end up with way too many background tasks running at once.
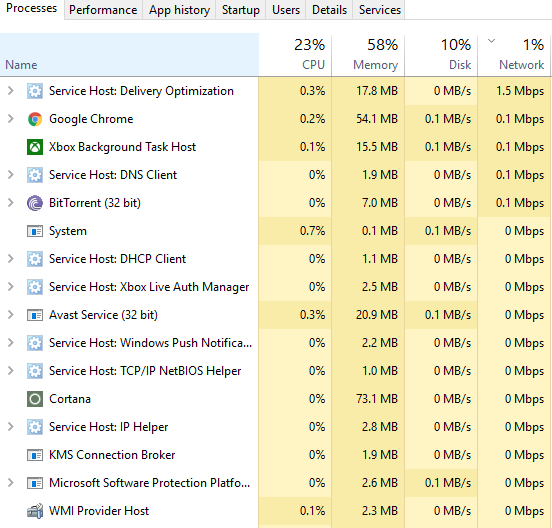
How to Find Out What’s Causing Slowdowns
To see exactly what’s running in the background, press Windows key + X, and then select “Task Manager.” From there, you can look under the Performance heading to see how much CPU time different applications are taking up. If you notice something unusual, you can use the “End task” button to stop the process and free up resources.
If you’re really worried about having too many background processes, consider disabling certain ones. For example, if you don’t use Microsoft Office 365, you can disable its automatic update feature.
Does the System Idle Process make a lot of use of the CPU?
The System Idle Process is a thread that runs under the control of the operating system. When a computer starts up, the OS creates multiple threads to handle different tasks. These threads are known as processes. A process is the unit of execution within an application. For example, when you open Microsoft Word, you start a new instance of the program. Each instance of the program is a separate process.
If no programs are running, there are no active processes. If one or more programs are running, however, the OS creates additional threads to execute each program. These threads are known collectively as processes.
When you close a program, the OS stops executing code associated with the program and frees resources allocated to the program. However, the OS does not stop executing code associated with the System Idle Process. In fact, the OS continues to execute code associated with the System Idle Process while the program is closed.
This happens because the OS needs to keep track of what applications are still running. If the OS stopped executing code associated with the idle process, the OS could not tell whether another application was running.
For example, imagine that you had three instances of Internet Explorer open, each of which contained a web browser window. You shut down one of those browsers. Now, without the idle process, the operating system cannot determine which browser is still running.
Without knowing which browser is still running, the operating system cannot properly clean up memory associated with the browser and free resources dedicated to the browser. As a result, the next time you launch a browser, the browser might crash due to lack of memory.